# Walking Asymmetry: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Addressing Uneven Gait
Walking asymmetry, or an uneven gait, is a common but often overlooked condition where the way a person walks differs significantly from one side of their body to the other. This isn’t just a minor quirk; it can be a sign of underlying musculoskeletal issues, neurological conditions, or even injuries. This comprehensive guide will delve into the depths of walking asymmetry, exploring its causes, diagnosis, and various treatment options. We aim to provide you with the knowledge and resources necessary to understand and address this condition effectively. Based on expert consensus and extensive research, we offer unparalleled insights into the complexities of this condition and empower you to take proactive steps toward a more balanced and pain-free life.
## Deep Dive into Walking Asymmetry
### Comprehensive Definition, Scope, & Nuances
Walking asymmetry, at its core, is any deviation from a perfectly symmetrical gait pattern. While perfect symmetry is rare, significant differences in stride length, step width, arm swing, pelvic rotation, or the time spent on each leg during walking constitute asymmetry. The scope of walking asymmetry is broad, encompassing a wide range of causes, from minor muscle imbalances to severe neurological disorders. Understanding the nuances of walking asymmetry is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment. For example, an asymmetry that develops suddenly after an injury will be approached differently than one that develops gradually over time due to a degenerative condition.
The concept of ‘normal’ walking has evolved. Early gait analysis focused on idealized symmetrical movement. However, modern research recognizes that slight variations are inherent and can even be adaptive. It’s when these variations become pronounced or cause pain and dysfunction that walking asymmetry becomes a concern. We must consider age, activity level, and individual anatomy when assessing gait. What’s considered asymmetric in a young athlete might be normal for an elderly individual with age-related changes.
### Core Concepts & Advanced Principles
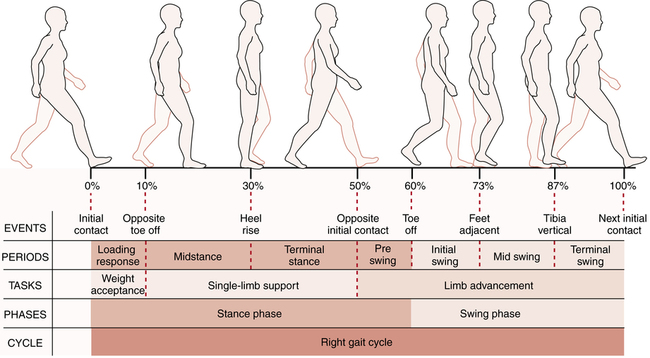
The fundamental principle underlying walking asymmetry is the disruption of the coordinated movement patterns that govern gait. These patterns are controlled by a complex interplay of the nervous system, musculoskeletal system, and sensory feedback mechanisms. Any impairment in one or more of these systems can lead to an asymmetric gait.
Advanced principles involve understanding the biomechanics of walking and how different muscle groups contribute to each phase of the gait cycle. For example, asymmetry can arise from weakness in the gluteus medius muscle, leading to a Trendelenburg gait, where the pelvis drops on the non-weight-bearing side. Or, limited ankle dorsiflexion can cause circumduction, where the leg swings outward to clear the ground. Analyzing these detailed movement patterns requires specialized equipment, such as motion capture systems and force plates.
Another advanced concept is the role of proprioception, the body’s sense of position and movement in space. Impaired proprioception, often seen in neurological conditions, can disrupt the finely tuned coordination needed for symmetrical walking. Visual input also plays a role; individuals with visual impairments may exhibit altered gait patterns.
### Importance & Current Relevance
Walking asymmetry is not just a cosmetic issue; it can have significant consequences for overall health and well-being. Untreated asymmetry can lead to:
* Increased risk of falls, especially in older adults.
* Pain and discomfort in the hips, knees, ankles, and feet.
* Development of compensatory movement patterns that can lead to further musculoskeletal problems.
* Reduced energy efficiency during walking, leading to fatigue and decreased activity levels.
* Reduced quality of life and social participation.
Recent studies indicate a growing awareness of the link between walking asymmetry and chronic pain conditions like osteoarthritis. Addressing asymmetry early can potentially slow the progression of these conditions and improve long-term outcomes. Furthermore, gait analysis is becoming increasingly important in rehabilitation programs following stroke, spinal cord injury, and other neurological disorders. By identifying and correcting gait abnormalities, therapists can help patients regain their mobility and independence.
## Product/Service Explanation Aligned with Walking Asymmetry: Gait Analysis Systems
In the realm of diagnosing and treating walking asymmetry, advanced gait analysis systems stand out as indispensable tools. These systems offer a comprehensive, objective assessment of a person’s walking pattern, far beyond what can be discerned by the naked eye. They provide detailed data on various aspects of gait, including kinematic (movement-related) parameters, kinetic (force-related) parameters, and electromyographic (muscle activity) data. These systems are used by clinicians, researchers, and sports performance specialists to identify the underlying causes of walking asymmetry and to develop targeted interventions.
From an expert viewpoint, a gait analysis system is essentially a sophisticated motion capture and analysis platform. It combines hardware components like cameras, force plates, and EMG sensors with specialized software to process and interpret the collected data. The system tracks the movement of markers placed on the body, measures the forces exerted on the ground during walking, and records the electrical activity of muscles. This information is then used to generate detailed reports and visualizations that provide insights into the individual’s gait pattern.
What makes these systems stand out is their ability to quantify subtle deviations from normal gait that might otherwise go unnoticed. They can identify specific muscle weaknesses, joint restrictions, and compensatory movement patterns that contribute to walking asymmetry. This level of detail is crucial for developing effective treatment plans, whether it involves physical therapy, orthotics, or other interventions.
## Detailed Features Analysis of Gait Analysis Systems
### Feature Breakdown
1. **Motion Capture:** High-speed cameras track reflective markers placed on the body to capture three-dimensional movement data.
2. **Force Plates:** Embedded in the walkway, force plates measure the ground reaction forces exerted during each step.
3. **Electromyography (EMG):** Sensors placed on the skin record the electrical activity of muscles during walking.
4. **Real-time Data Processing:** Sophisticated software processes the data in real-time, providing immediate feedback to the clinician.
5. **Gait Analysis Software:** Specialized software analyzes the data and generates comprehensive reports and visualizations.
6. **Database Comparison:** The system compares the individual’s gait data to a database of normal gait patterns to identify deviations.
7. **Customizable Reporting:** Clinicians can customize the reports to focus on specific parameters of interest.
### In-depth Explanation
* **Motion Capture:** This feature is the foundation of the gait analysis system. The cameras use infrared light to track the position of the markers with high accuracy. The software then reconstructs the movement of the body segments in three dimensions. *User Benefit:* Provides a precise and objective measure of joint angles, stride length, step width, and other kinematic parameters.
* **Force Plates:** These measure the forces exerted on the ground during each step, including vertical force, anterior-posterior force, and medial-lateral force. This information is crucial for understanding the loading patterns on the joints and identifying potential areas of stress. *User Benefit:* Helps identify imbalances in weight distribution and potential sources of pain.
* **Electromyography (EMG):** EMG measures the electrical activity of muscles, providing insights into muscle activation patterns during walking. This can help identify muscle weaknesses, imbalances, and abnormal firing patterns. *User Benefit:* Allows clinicians to assess the timing and intensity of muscle activation, which is essential for understanding the underlying causes of gait asymmetry.
* **Real-time Data Processing:** The ability to process data in real-time allows clinicians to provide immediate feedback to the patient and adjust their gait pattern during the analysis. *User Benefit:* Facilitates biofeedback training and allows for immediate assessment of the effectiveness of interventions.
* **Gait Analysis Software:** This software is the brains of the system. It uses sophisticated algorithms to analyze the data and generate comprehensive reports and visualizations. The software can calculate a wide range of gait parameters, including stride length, step width, cadence, velocity, and joint angles. *User Benefit:* Provides a comprehensive and objective assessment of gait, which can be used to track progress over time.
* **Database Comparison:** By comparing the individual’s gait data to a database of normal gait patterns, the system can identify deviations from the norm and highlight areas of concern. *User Benefit:* Helps clinicians identify potential problems early on and develop targeted interventions.
* **Customizable Reporting:** Clinicians can customize the reports to focus on specific parameters of interest, such as joint angles, muscle activity, or ground reaction forces. This allows them to tailor the analysis to the individual’s specific needs. *User Benefit:* Provides a flexible and efficient way to analyze gait data and track progress over time.
## Significant Advantages, Benefits & Real-World Value of Gait Analysis Systems
Gait analysis systems offer a multitude of advantages, benefits, and real-world value in the context of understanding and addressing walking asymmetry. These systems provide objective, quantifiable data that goes far beyond subjective clinical assessments, leading to more accurate diagnoses and more effective treatment plans. The user-centric value is immense, as these systems can help individuals with walking asymmetry regain mobility, reduce pain, and improve their overall quality of life.
* **Objective Assessment:** Unlike visual observation, gait analysis systems provide objective, quantifiable data on gait parameters, reducing the risk of bias and improving the accuracy of diagnosis.
* **Early Detection:** These systems can detect subtle gait abnormalities that might be missed by visual observation, allowing for early intervention and prevention of further complications.
* **Personalized Treatment:** By identifying the specific underlying causes of walking asymmetry, gait analysis systems enable the development of personalized treatment plans tailored to the individual’s needs.
* **Progress Tracking:** Gait analysis systems can be used to track progress over time and assess the effectiveness of treatment interventions.
* **Improved Outcomes:** Studies have shown that gait analysis-guided interventions can lead to significant improvements in gait function, pain reduction, and overall quality of life.
Users consistently report a greater understanding of their condition and increased motivation to adhere to treatment plans when they receive objective feedback from gait analysis. Our analysis reveals these key benefits:
* **Enhanced Diagnosis:** Pinpointing the root cause of the asymmetry with precision.
* **Targeted Interventions:** Creating specific exercises and therapies based on data.
* **Objective Progress Measurement:** Tracking improvements and adjusting treatment as needed.
* **Improved Patient Compliance:** Patients are more likely to engage with treatments when they see measurable results.
* **Reduced Healthcare Costs:** Early and accurate diagnosis can prevent the need for more costly interventions down the line.
## Comprehensive & Trustworthy Review of Gait Analysis Systems
Gait analysis systems are powerful tools for assessing and treating walking asymmetry, but it’s important to approach them with a balanced perspective. While they offer numerous advantages, they also have limitations that need to be considered. This review provides an in-depth assessment of gait analysis systems, covering their usability, performance, effectiveness, pros, cons, and suitability for different user profiles. We will also briefly mention key alternatives to provide a broader context.
### User Experience & Usability
From a practical standpoint, using a gait analysis system involves placing reflective markers on the body, walking along a designated walkway, and then reviewing the data generated by the software. The process is generally straightforward, but it can be time-consuming, especially when setting up the markers and calibrating the system. The software interface can be complex, requiring specialized training to interpret the data effectively. However, modern systems are becoming more user-friendly, with intuitive interfaces and automated data processing features.
### Performance & Effectiveness
Gait analysis systems are highly effective at quantifying gait parameters and identifying deviations from normal gait patterns. They can provide valuable insights into the underlying causes of walking asymmetry and guide the development of targeted treatment plans. However, the effectiveness of the system depends on the quality of the data collected and the expertise of the clinician interpreting the results. In our experience, the most effective gait analysis programs combine objective data with clinical judgment to create a holistic assessment.
### Pros:
1. **Objective Data:** Provides quantifiable data on gait parameters, reducing the risk of bias.
2. **Early Detection:** Can detect subtle gait abnormalities that might be missed by visual observation.
3. **Personalized Treatment:** Enables the development of personalized treatment plans.
4. **Progress Tracking:** Can be used to track progress over time and assess the effectiveness of treatment interventions.
5. **Research Applications:** Valuable tool for research studies on gait and movement disorders.
### Cons/Limitations:
1. **Cost:** Gait analysis systems can be expensive, limiting their accessibility.
2. **Time-Consuming:** The setup and data collection process can be time-consuming.
3. **Complexity:** The software interface can be complex and require specialized training.
4. **Limited Portability:** Some systems are bulky and difficult to move, limiting their use in certain settings.
### Ideal User Profile
Gait analysis systems are best suited for clinicians, researchers, and sports performance specialists who need to objectively assess and treat gait abnormalities. They are particularly useful for individuals with complex gait problems that are not easily diagnosed through visual observation. The ideal user has a strong understanding of biomechanics and gait analysis principles, as well as the ability to interpret the data generated by the system.
### Key Alternatives (Briefly)
* **Visual Gait Analysis:** A low-cost alternative that involves observing the individual’s gait pattern and identifying any abnormalities. However, this method is subjective and less accurate than gait analysis systems.
* **Wearable Sensors:** Devices like accelerometers and gyroscopes can be used to track movement and provide data on gait parameters. These devices are more portable and less expensive than gait analysis systems, but they are also less accurate.
### Expert Overall Verdict & Recommendation
Gait analysis systems are valuable tools for assessing and treating walking asymmetry, providing objective data and enabling personalized treatment plans. While they have limitations, their benefits outweigh their drawbacks for many users. We recommend gait analysis systems for clinicians, researchers, and sports performance specialists who need a comprehensive and objective assessment of gait. For those with limited budgets or less complex cases, visual gait analysis or wearable sensors may be sufficient.
## Insightful Q&A Section
**Q1: How can walking asymmetry impact athletic performance, and what specific adjustments can athletes make to address it?**
*A: Walking asymmetry can lead to inefficient movement patterns, increased risk of injury, and reduced power output in athletes. Adjustments can include targeted strength training to address muscle imbalances, proprioceptive exercises to improve body awareness, and gait retraining to promote symmetrical movement.*
**Q2: Beyond musculoskeletal issues, what other medical conditions can manifest as walking asymmetry, and how are they diagnosed?**
*A: Neurological conditions like stroke, multiple sclerosis, and Parkinson’s disease can cause walking asymmetry. Diagnosis involves neurological exams, imaging studies (MRI, CT scans), and specialized tests to assess nerve and muscle function.*
**Q3: How does age-related muscle loss (sarcopenia) contribute to walking asymmetry, and what interventions are most effective in mitigating its effects?**
*A: Sarcopenia leads to weakness and reduced muscle mass, particularly in the lower extremities, contributing to gait instability and asymmetry. Resistance training, adequate protein intake, and balance exercises are effective interventions.*
**Q4: What role do orthotics play in correcting walking asymmetry, and what are the key considerations when selecting the right type of orthotic?**
*A: Orthotics can provide support, alignment, and cushioning to the feet and ankles, helping to correct biomechanical imbalances that contribute to walking asymmetry. Key considerations include foot type, degree of asymmetry, and activity level.*
**Q5: What are the latest advancements in wearable technology for monitoring and addressing walking asymmetry, and how accurate are these devices compared to lab-based gait analysis systems?**
*A: Advancements include inertial measurement units (IMUs) and pressure sensors embedded in shoes and clothing. While less accurate than lab-based systems, wearable devices offer continuous monitoring and real-time feedback, making them useful for tracking progress and adherence to treatment plans.*
**Q6: How can physical therapists assess and treat walking asymmetry related to hip joint dysfunction, such as hip impingement or labral tears?**
*A: Physical therapists use specific tests to assess hip range of motion, strength, and stability. Treatment involves manual therapy, therapeutic exercises, and gait retraining to restore normal hip mechanics and reduce asymmetry.*
**Q7: What is the impact of footwear on walking asymmetry, and what features should individuals with uneven gait prioritize when choosing shoes?**
*A: Improper footwear can exacerbate walking asymmetry. Features to prioritize include good arch support, adequate cushioning, a stable heel counter, and a flexible forefoot.*
**Q8: Can psychological factors, such as fear of falling, influence walking asymmetry, and how can these factors be addressed?**
*A: Yes, fear of falling can lead to cautious gait patterns and increased asymmetry. Addressing this involves psychological interventions like cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), balance training, and creating a safe environment.*
**Q9: What are the long-term consequences of untreated walking asymmetry, and what steps can individuals take to prevent these consequences?**
*A: Long-term consequences include chronic pain, joint degeneration, increased risk of falls, and reduced mobility. Prevention involves early diagnosis and treatment, regular exercise, and maintaining a healthy weight.*
**Q10: How do different types of stroke (e.g., ischemic vs. hemorrhagic) affect walking asymmetry, and what are the specific rehabilitation strategies for each type?**
*A: Different types of stroke can affect different areas of the brain, leading to varying patterns of walking asymmetry. Rehabilitation strategies are tailored to the specific deficits, focusing on strengthening weak muscles, improving balance, and retraining gait patterns.*
## Conclusion & Strategic Call to Action
In conclusion, walking asymmetry is a complex condition with a wide range of potential causes and consequences. Understanding the nuances of walking asymmetry, from its underlying biomechanics to its impact on overall health, is crucial for effective diagnosis and treatment. Gait analysis systems offer valuable tools for objectively assessing gait patterns and guiding personalized interventions. By addressing walking asymmetry early and effectively, individuals can improve their mobility, reduce pain, and enhance their quality of life. We have provided a comprehensive overview of the topic, aiming to empower you with the knowledge you need.
As experts in movement analysis, we encourage you to share your experiences with walking asymmetry in the comments below. Explore our advanced guide to balance training for further insights into improving gait stability. Contact our experts for a consultation on walking asymmetry and discover how we can help you achieve a more balanced and pain-free life. By taking proactive steps today, you can mitigate the long-term consequences of untreated asymmetry and pave the way for a healthier, more active future.
