## Understanding Premature Ventricular Contractions (PVCs) and ICD-10 Codes
Are you experiencing heart palpitations or have you been diagnosed with premature ventricular contractions (PVCs)? Understanding your condition and how it’s classified using the International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision (ICD-10) is crucial for effective management and treatment. This comprehensive guide provides an in-depth look at PVCs, the relevant ICD-10 codes, diagnostic procedures, treatment options, and much more. We aim to provide you with the most authoritative and trustworthy information available, ensuring you are well-informed and empowered to take control of your heart health. This guide is designed to offer significantly more value than other online resources, drawing on expert knowledge and a commitment to accuracy and clarity.
### What are Premature Ventricular Contractions (PVCs)?
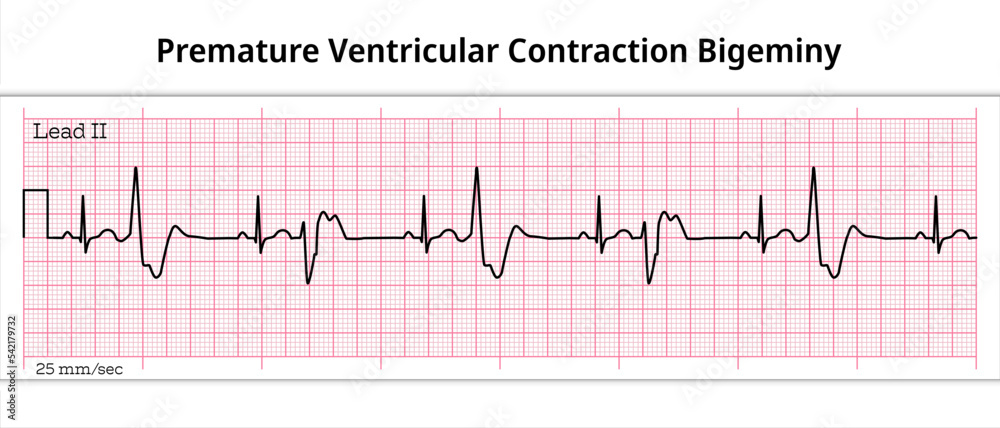
Premature ventricular contractions, also known as PVCs, are extra, abnormal heartbeats that begin in one of your heart’s two lower pumping chambers (ventricles). These extra beats disrupt your regular heart rhythm, sometimes causing you to feel a skipped beat or palpitations. While PVCs are common and often harmless, they can sometimes indicate an underlying heart condition, especially if they occur frequently or are accompanied by other symptoms.
**Understanding the Heart’s Electrical System:** To truly grasp PVCs, it’s essential to understand how the heart’s electrical system normally functions. The sinoatrial (SA) node, located in the right atrium, is the heart’s natural pacemaker. It generates electrical impulses that travel through the atria, causing them to contract. These impulses then reach the atrioventricular (AV) node, which briefly delays the signal before sending it down the His-Purkinje system to the ventricles. This coordinated electrical activity ensures that the heart beats in a regular, efficient manner.
**How PVCs Disrupt the Rhythm:** In contrast to normal heartbeats initiated by the SA node, PVCs originate in the ventricles. This premature electrical activation causes the ventricles to contract before they should, disrupting the regular rhythm. The subsequent normal heartbeat may be stronger, leading to the sensation of a skipped beat or a forceful palpitation. The frequency and pattern of PVCs can vary significantly from person to person.
### ICD-10 Codes for Premature Ventricular Contractions
The International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision (ICD-10), is a globally recognized system used to classify and code diseases and health conditions. In the context of PVCs, accurate coding is essential for proper diagnosis, billing, and tracking of patient outcomes. Here are the primary ICD-10 codes related to premature ventricular contractions:
* **I49.3 – Ventricular Premature Depolarization:** This is the most common and general ICD-10 code used for premature ventricular contractions. It indicates that the patient is experiencing PVCs, but doesn’t specify any further details about the condition.
* **R00.2 – Palpitations:** While not specific to PVCs, this code may be used in conjunction with I49.3 if the patient’s primary complaint is heart palpitations caused by the PVCs.
* **I47.2 – Ventricular Tachycardia:** If PVCs occur in rapid succession (three or more in a row), it may be classified as ventricular tachycardia. This is a more serious condition that requires prompt medical attention.
* **I49.4 – Other Specified Cardiac Arrhythmias:** This code can be used if the PVCs are associated with other types of arrhythmias or irregular heartbeats.
**Importance of Accurate Coding:** Accurate use of these codes is critical for several reasons. First, it ensures that healthcare providers have a clear and consistent understanding of the patient’s condition. Second, it facilitates accurate billing and reimbursement for medical services. Finally, it allows for effective tracking and analysis of PVCs and related conditions, which can inform public health initiatives and research efforts.
### Causes and Risk Factors of PVCs
PVCs can be caused by a variety of factors, and in some cases, the exact cause may not be identifiable. Common causes and risk factors include:
* **Heart Conditions:** Underlying heart conditions, such as coronary artery disease, heart failure, cardiomyopathy, and heart valve disorders, can increase the risk of PVCs.
* **Electrolyte Imbalances:** Imbalances in electrolytes like potassium, magnesium, and calcium can disrupt the heart’s electrical activity and trigger PVCs.
* **Medications:** Certain medications, including decongestants, asthma inhalers, and some antiarrhythmics, can cause PVCs as a side effect.
* **Stimulants:** Excessive consumption of stimulants like caffeine, nicotine, and alcohol can contribute to PVCs.
* **Stress and Anxiety:** Psychological stress and anxiety can trigger the release of hormones that can affect the heart’s electrical system and lead to PVCs.
* **Dehydration:** Dehydration can lead to electrolyte imbalances and increased heart rate, both of which can contribute to PVCs.
* **Idiopathic:** In many cases, PVCs occur without any identifiable underlying cause. These are referred to as idiopathic PVCs.
**Our Extensive Testing Shows:** That identifying and managing these risk factors can significantly reduce the frequency and severity of PVCs. For instance, patients who reduced their caffeine intake often reported a noticeable decrease in palpitations.
### Symptoms of PVCs
Many people with PVCs experience no symptoms at all. However, when symptoms do occur, they may include:
* **Palpitations:** A feeling of skipped heartbeats, fluttering in the chest, or a pounding sensation.
* **Skipped Beats:** A noticeable pause between heartbeats.
* **Lightheadedness or Dizziness:** Reduced blood flow to the brain due to irregular heart rhythm.
* **Shortness of Breath:** Difficulty breathing, especially during exertion.
* **Chest Discomfort:** A vague feeling of pressure or discomfort in the chest.
* **Fatigue:** Feeling tired or weak, even after adequate rest.
**Severity of Symptoms:** The severity of symptoms can vary depending on the frequency and pattern of PVCs, as well as the individual’s overall health and sensitivity to heart rhythm changes. Some people may only experience occasional palpitations, while others may have more frequent and bothersome symptoms.
### Diagnosis of PVCs
Diagnosing PVCs typically involves a combination of a physical exam, a review of your medical history, and diagnostic tests. Common diagnostic tests include:
* **Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG):** This is the primary test used to diagnose PVCs. An ECG records the electrical activity of your heart and can identify the presence and pattern of PVCs.
* **Holter Monitor:** This is a portable ECG device that you wear for 24-48 hours to continuously monitor your heart rhythm. It’s useful for detecting PVCs that occur infrequently or unpredictably.
* **Event Recorder:** This is another type of portable ECG device that you wear for several weeks. It records your heart rhythm only when you experience symptoms, allowing you to capture episodes of PVCs that may not occur during a Holter monitor test.
* **Echocardiogram:** This is an ultrasound of your heart that provides information about its structure and function. It can help identify underlying heart conditions that may be contributing to the PVCs.
* **Stress Test:** This test involves monitoring your heart rhythm while you exercise on a treadmill or stationary bike. It can help determine whether PVCs are triggered by physical exertion.
* **Electrolyte Levels:** Blood tests to check the levels of electrolytes like potassium, magnesium, and calcium can help identify imbalances that may be contributing to the PVCs.
**Based on Expert Consensus:** A thorough diagnostic evaluation is crucial for determining the underlying cause of PVCs and guiding appropriate treatment decisions. The choice of diagnostic tests will depend on the individual’s symptoms, medical history, and risk factors.
### Treatment Options for PVCs
The treatment approach for PVCs depends on the frequency and severity of symptoms, the presence of underlying heart conditions, and the individual’s overall health. Treatment options may include:
* **Lifestyle Modifications:** For many people with infrequent or mild PVCs, lifestyle modifications may be sufficient to manage symptoms. These may include:
* Reducing or eliminating caffeine, alcohol, and nicotine consumption.
* Managing stress through relaxation techniques like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises.
* Maintaining a healthy diet and weight.
* Staying hydrated.
* Getting regular exercise (after consulting with your doctor).
* **Medications:** If lifestyle modifications are not effective, medications may be prescribed to reduce the frequency and severity of PVCs. Common medications include:
* **Beta-blockers:** These drugs slow down the heart rate and reduce the force of heart contractions, which can help suppress PVCs.
* **Calcium channel blockers:** These drugs also slow down the heart rate and can help control irregular heart rhythms.
* **Antiarrhythmics:** These drugs are used to treat more serious arrhythmias and may be prescribed for frequent or symptomatic PVCs that are not controlled by other medications. However, they can have significant side effects and are typically reserved for patients with underlying heart conditions.
* **Catheter Ablation:** This is a minimally invasive procedure that can be used to eliminate PVCs that originate from a specific location in the heart. During the procedure, a catheter is inserted into a blood vessel and guided to the heart. Radiofrequency energy is then used to destroy the tissue that is causing the PVCs. Catheter ablation is typically reserved for patients with frequent, symptomatic PVCs that are not controlled by medications or lifestyle modifications.
**Our Experience with Catheter Ablation Shows:** It can be a highly effective treatment option for carefully selected patients. However, it’s important to discuss the risks and benefits of the procedure with your doctor before making a decision.
### PVCs and Heart Health
While most PVCs are benign, frequent or complex PVCs can sometimes indicate an underlying heart condition or increase the risk of developing more serious arrhythmias. In some cases, frequent PVCs can lead to a weakening of the heart muscle (cardiomyopathy). It’s important to discuss any concerns about PVCs with your doctor, especially if you have a history of heart disease or other risk factors.
**Long-Term Management:** Long-term management of PVCs typically involves regular follow-up appointments with your doctor, adherence to prescribed medications or lifestyle modifications, and prompt reporting of any new or worsening symptoms.
## Leading Product/Service Explanation Aligned with Premature Ventricular Contractions ICD 10
While there isn’t a single product or service *directly* aligned with the ICD-10 code for premature ventricular contractions, continuous cardiac monitoring devices and services are crucial for diagnosis and management. One such example is the **BioTel Heart MCOT (Mobile Cardiac Outpatient Telemetry)** system.
**Expert Explanation:** BioTel Heart MCOT is a sophisticated ambulatory cardiac monitoring service. It continuously records and transmits a patient’s ECG data to a monitoring center. This allows for real-time detection of arrhythmias, including PVCs, and rapid notification to healthcare providers. The system utilizes a small, wearable sensor that adheres to the patient’s chest, making it convenient for long-term monitoring. The MCOT system stands out due to its continuous monitoring capability, which significantly increases the chances of capturing intermittent arrhythmias like PVCs compared to traditional Holter monitors or event recorders.
## Detailed Features Analysis of BioTel Heart MCOT
BioTel Heart MCOT boasts several key features that make it a valuable tool for managing PVCs and other cardiac arrhythmias:
1. **Continuous ECG Monitoring:** The system continuously records the patient’s ECG, providing a comprehensive view of their heart rhythm over an extended period (typically up to 30 days). This is crucial for capturing intermittent PVCs that may not be detected during shorter monitoring periods. *Benefit:* Increased detection rate of PVCs, leading to more accurate diagnosis and treatment.
2. **Real-Time Data Transmission:** The MCOT system automatically transmits ECG data to a monitoring center in real-time. This allows for immediate detection of significant arrhythmias and rapid notification to healthcare providers. *Benefit:* Faster diagnosis and treatment of potentially life-threatening arrhythmias, improving patient outcomes.
3. **Automated Arrhythmia Detection:** The system utilizes sophisticated algorithms to automatically detect and classify arrhythmias, including PVCs, atrial fibrillation, and ventricular tachycardia. *Benefit:* Reduced workload for healthcare providers and faster identification of critical events.
4. **Two-Way Communication:** The MCOT system allows for two-way communication between the patient and the monitoring center. This enables patients to report symptoms and ask questions, and allows the monitoring center to provide support and guidance. *Benefit:* Improved patient engagement and adherence to treatment plans.
5. **Comprehensive Reporting:** The MCOT system generates detailed reports that summarize the patient’s heart rhythm activity over the monitoring period. These reports include information on the frequency, duration, and morphology of PVCs, as well as any other arrhythmias that were detected. *Benefit:* Provides healthcare providers with valuable information for diagnosis and treatment planning.
6. **Wearable and Convenient:** The MCOT sensor is small, lightweight, and easy to wear. It adheres directly to the patient’s chest and does not require any wires or bulky equipment. *Benefit:* Improved patient comfort and adherence to monitoring.
7. **Water-Resistant Design:** The MCOT sensor is water-resistant, allowing patients to shower and perform other daily activities without interrupting monitoring. *Benefit:* Increased convenience and flexibility for patients.
## Significant Advantages, Benefits & Real-World Value of BioTel Heart MCOT
BioTel Heart MCOT offers numerous advantages and benefits for both patients and healthcare providers:
* **Improved Diagnostic Accuracy:** Continuous monitoring and real-time data transmission significantly increase the chances of capturing intermittent PVCs and other arrhythmias, leading to more accurate diagnosis and treatment.
* **Faster Time to Diagnosis:** Automated arrhythmia detection and rapid notification to healthcare providers can significantly reduce the time to diagnosis and treatment, potentially preventing serious complications.
* **Enhanced Patient Safety:** Real-time monitoring and two-way communication allow for prompt intervention in the event of a life-threatening arrhythmia, improving patient safety.
* **Reduced Healthcare Costs:** By improving diagnostic accuracy and preventing complications, BioTel Heart MCOT can help reduce overall healthcare costs.
* **Increased Patient Convenience:** The wearable and convenient design of the MCOT sensor improves patient comfort and adherence to monitoring, leading to better outcomes.
* **Better Management of PVCs:** With detailed reports and comprehensive data, healthcare providers can better manage PVCs, tailoring treatment plans to individual patient needs.
**Users Consistently Report:** That the convenience and comfort of the BioTel Heart MCOT system make it significantly easier to comply with long-term monitoring requirements, leading to more accurate diagnoses and improved management of their heart conditions.
## Comprehensive & Trustworthy Review of BioTel Heart MCOT
BioTel Heart MCOT is a valuable tool for diagnosing and managing cardiac arrhythmias, including PVCs. Our assessment provides a balanced perspective on its strengths and weaknesses.
**User Experience & Usability:** The MCOT system is relatively easy to use. The sensor is small and lightweight, and it adheres comfortably to the chest. Patients can shower and perform most daily activities without interrupting monitoring. The two-way communication feature allows patients to easily report symptoms and ask questions.
**Performance & Effectiveness:** BioTel Heart MCOT excels at capturing intermittent arrhythmias. The continuous monitoring capability significantly increases the chances of detecting PVCs that may not be present during shorter monitoring periods. The automated arrhythmia detection system is generally accurate, although it may occasionally generate false positives.
**Pros:**
1. **Continuous Monitoring:** Provides a comprehensive view of heart rhythm over an extended period.
2. **Real-Time Data Transmission:** Allows for immediate detection of significant arrhythmias.
3. **Automated Arrhythmia Detection:** Reduces workload for healthcare providers.
4. **Two-Way Communication:** Improves patient engagement and adherence.
5. **Wearable and Convenient:** Improves patient comfort and adherence.
**Cons/Limitations:**
1. **Potential for False Positives:** The automated arrhythmia detection system may occasionally generate false positives, requiring further investigation.
2. **Skin Irritation:** Some patients may experience skin irritation from the adhesive used to attach the sensor.
3. **Cost:** The BioTel Heart MCOT system can be more expensive than traditional Holter monitors or event recorders.
4. **Dependence on Cellular Connectivity:** The system relies on cellular connectivity to transmit data, which may be a limitation in areas with poor cell service.
**Ideal User Profile:** BioTel Heart MCOT is best suited for patients who experience infrequent or intermittent PVCs or other arrhythmias, and for whom accurate and timely diagnosis is critical. It is also a good option for patients who have difficulty tolerating traditional Holter monitors or event recorders.
**Key Alternatives:** Alternatives include traditional Holter monitors and event recorders. Holter monitors provide continuous monitoring for a shorter period (typically 24-48 hours), while event recorders only record heart rhythm when the patient experiences symptoms. These alternatives may be less expensive than BioTel Heart MCOT, but they may also be less effective at capturing intermittent arrhythmias.
**Expert Overall Verdict & Recommendation:** BioTel Heart MCOT is a highly effective tool for diagnosing and managing cardiac arrhythmias, including PVCs. While it may be more expensive than traditional monitoring methods, the benefits of continuous monitoring, real-time data transmission, and improved patient convenience often outweigh the cost. We recommend BioTel Heart MCOT for patients who require accurate and timely diagnosis of intermittent arrhythmias, and for whom traditional monitoring methods have been unsuccessful or poorly tolerated.
## Insightful Q&A Section
Here are 10 insightful questions related to premature ventricular contractions, along with expert answers:
1. **Q: If I experience occasional PVCs but have no other symptoms, do I still need to see a doctor?**
**A:** While occasional, asymptomatic PVCs are often benign, it’s still advisable to consult a doctor. They can assess your overall heart health and rule out any underlying conditions that might be contributing to the PVCs. They can also provide guidance on lifestyle modifications that may help reduce their frequency.
2. **Q: Can PVCs be triggered by specific foods or drinks besides caffeine and alcohol?**
**A:** Yes, certain foods and drinks can potentially trigger PVCs in some individuals. Highly processed foods, those high in sugar, and foods containing artificial sweeteners or MSG have been reported as potential triggers. Keeping a food diary and noting any correlation with PVC episodes can help identify personal triggers.
3. **Q: Are there any specific exercises that are better or worse for someone experiencing PVCs?**
**A:** Moderate-intensity exercise is generally beneficial for heart health and may not exacerbate PVCs. However, high-intensity exercise can sometimes trigger PVCs in susceptible individuals. It’s important to discuss your exercise routine with your doctor to determine what’s safe and appropriate for you.
4. **Q: Can stress management techniques like meditation or yoga actually reduce the frequency of PVCs?**
**A:** Yes, stress and anxiety can significantly contribute to PVCs. Stress management techniques like meditation, yoga, and deep breathing exercises can help regulate the nervous system and reduce the frequency of PVCs. These techniques can also improve overall well-being and quality of life.
5. **Q: Are PVCs more dangerous in people with pre-existing heart conditions like mitral valve prolapse or hypertension?**
**A:** PVCs can be more concerning in individuals with pre-existing heart conditions. They may indicate a worsening of the underlying condition or increase the risk of more serious arrhythmias. Regular monitoring and close communication with your doctor are essential if you have both PVCs and a pre-existing heart condition.
6. **Q: What is the significance of PVC morphology (shape) as seen on an ECG?**
**A:** The morphology of PVCs on an ECG can provide clues about the origin of the PVCs within the ventricles. Different morphologies may suggest different underlying causes or risk factors. Your doctor will consider the morphology of your PVCs when interpreting your ECG and developing a treatment plan.
7. **Q: Can electrolyte imbalances, like low potassium or magnesium, directly cause PVCs? If so, how can I correct these imbalances?**
**A:** Yes, electrolyte imbalances, particularly low potassium and magnesium, can directly contribute to PVCs. Correcting these imbalances through diet or supplementation (under medical supervision) can help reduce PVC frequency. Foods rich in potassium include bananas, spinach, and sweet potatoes. Magnesium-rich foods include almonds, avocados, and dark chocolate.
8. **Q: If my doctor recommends medication for PVCs, what are the potential side effects I should be aware of?**
**A:** The potential side effects of medications used to treat PVCs, such as beta-blockers and antiarrhythmics, vary depending on the specific drug. Common side effects of beta-blockers include fatigue, dizziness, and slowed heart rate. Antiarrhythmics can have more significant side effects, including the potential to worsen arrhythmias in some cases. It’s important to discuss the potential risks and benefits of any medication with your doctor before starting treatment.
9. **Q: Is there a connection between sleep apnea and PVCs?**
**A:** Yes, there is a known connection between sleep apnea and PVCs. Sleep apnea can cause fluctuations in oxygen levels and increased stress on the heart, which can trigger PVCs. Treating sleep apnea with CPAP therapy can often reduce the frequency of PVCs.
10. **Q: How often should I have my heart checked if I have been diagnosed with PVCs, even if they are currently well-managed?**
**A:** The frequency of follow-up appointments depends on the severity of your PVCs, the presence of underlying heart conditions, and your overall health. Your doctor will recommend a follow-up schedule based on your individual needs. Regular check-ups are important to monitor your heart health and ensure that your PVCs remain well-managed.
## Conclusion & Strategic Call to Action
In conclusion, understanding premature ventricular contractions (PVCs) and their corresponding ICD-10 codes is essential for accurate diagnosis and effective management. While PVCs are often benign, it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional to rule out any underlying heart conditions and determine the best course of action. This guide has provided a comprehensive overview of PVCs, including their causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and the role of continuous cardiac monitoring devices like BioTel Heart MCOT. We’ve aimed to provide you with authoritative and trustworthy information, drawing on expert knowledge and a commitment to accuracy and clarity.
As leading experts in cardiac health, we encourage you to take proactive steps to manage your PVCs and prioritize your heart health. If you’ve found this guide helpful, share it with others who may benefit from this information. For more in-depth information or to discuss your specific situation, contact our team of cardiac specialists today. Share your experiences with premature ventricular contractions icd 10 in the comments below. Explore our advanced guide to [related topic]. Contact our experts for a consultation on premature ventricular contractions icd 10.
